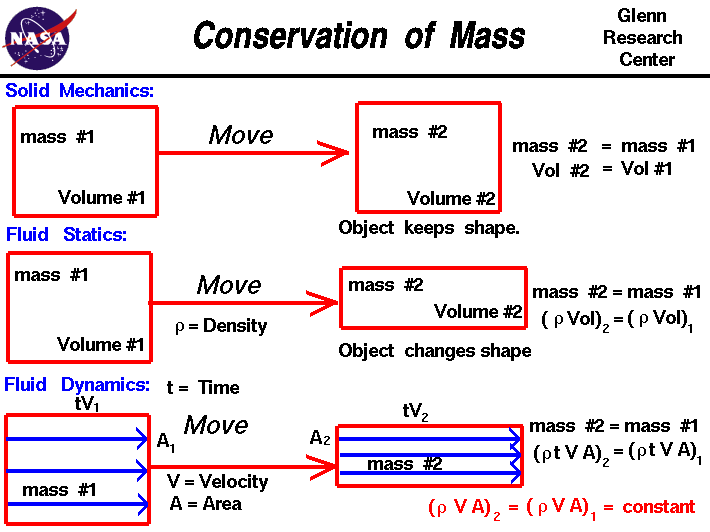
Mass: the amount of matter in an object.
Example:
Volume: the amount of space an object takes up.
Example:
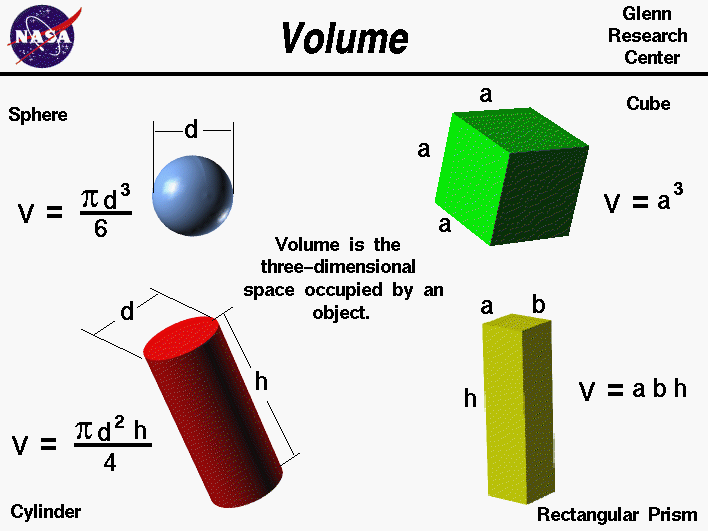
Weight: (on Earth) a measure of the force of gravity between Earth and an object.
Example:

Density: a measure of how tightly packed matter is; the amount of mass contained in a given volume.
Example:

Buoyancy: the upward push on an object by the liquid (or gas) the object is placed in.
Example:

Conduct: allow heat or electricity to flow through readily.
Example:

Insulate: not allow heat or electricity to flow through readily.
Example:

Vocabulary page 306
Element: a basic building block of matter; a pure substance that cannot be broken down into anything simpler.
Example:

Compound: a chemical combination of two or more elements into a single substance.
Example:

Atom: the smallest unit of an element that still has the properties of the element.
Example:
Proton: a particle with a positive charge in the nucleus of an atom.
Example:

Neutron: an uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom.
Example:

Electron: a particle with a negative charge moving around the nucleus of an atom.
Example:

Nucleus: the dense center part of an atom.
Example

Molecule: a group of more than one atom joined together that acts like a single particle.
Example:

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario